Biphasic P Wave in V1: Anatomy & Electrophysiology
Nov 04, 2025Related topics:
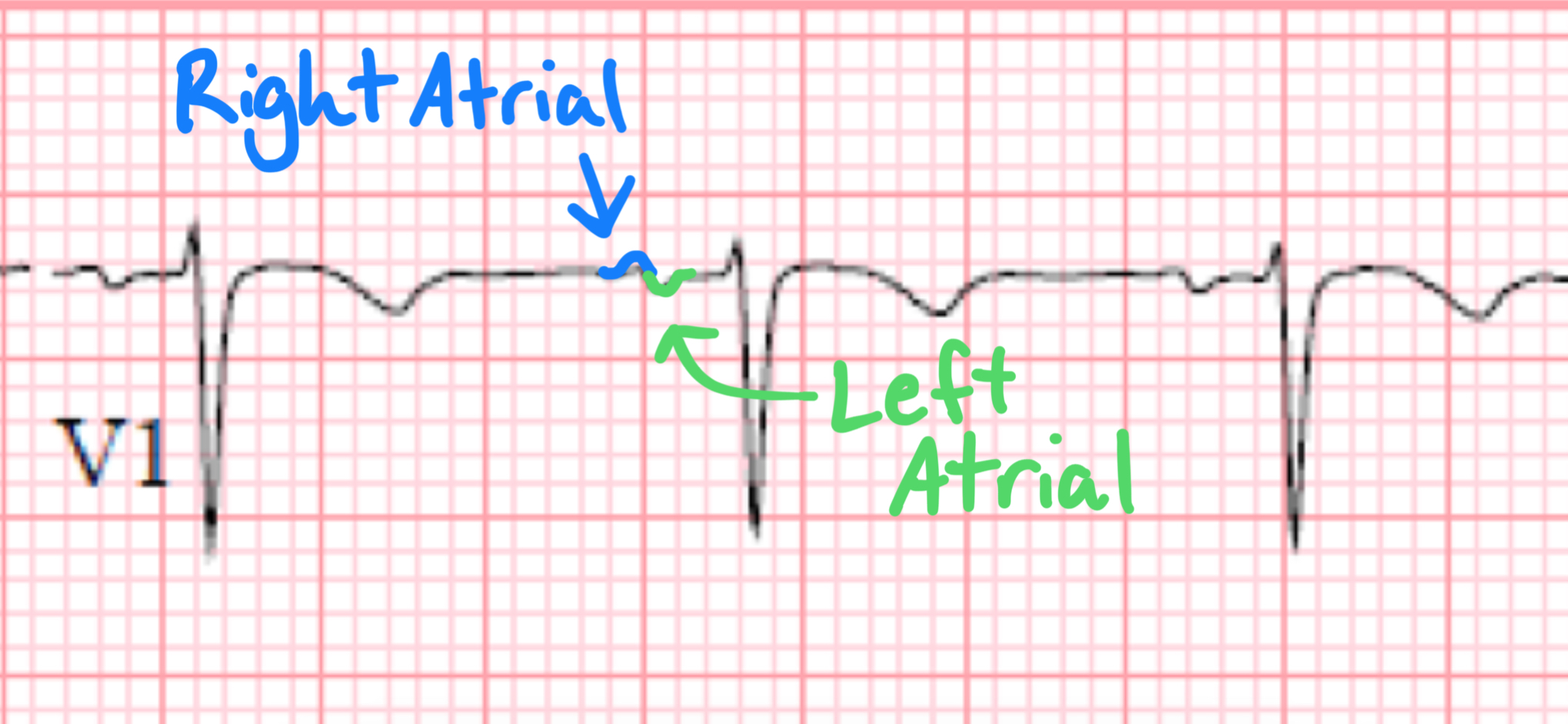
In lead V1, the P wave often appears biphasic, reflecting the sequential depolarization of the right and left atria. This morphology is due to the anatomical positioning of the sinoatrial (SA) node in the right atrium, where atrial depolarization begins and then spreads toward the left atrium.
- Since V1 is positioned near the right atrium, the initial portion of the P wave (right atrial depolarization) is directed toward V1, creating an initial positive deflection.
- However, as the depolarization wave reaches the left atrium, its vector shifts away from V1, generating a subsequent negative deflection.

This results in a characteristic biphasic P wave, where the first (positive) portion represents right atrial activation, and the second (negative) portion represents left atrial activation. If the negative component of the P wave is significantly enlarged or prolonged, it may indicate left atrial enlargement (LAE), as seen in conditions like mitral valve disease, left ventricular dysfunction or chronic hypertension.
Enjoy ECG Lectures with Reid? Here is a special gift from Reid
100 High Yield Annotated ECGs
Click below to download this free resource.